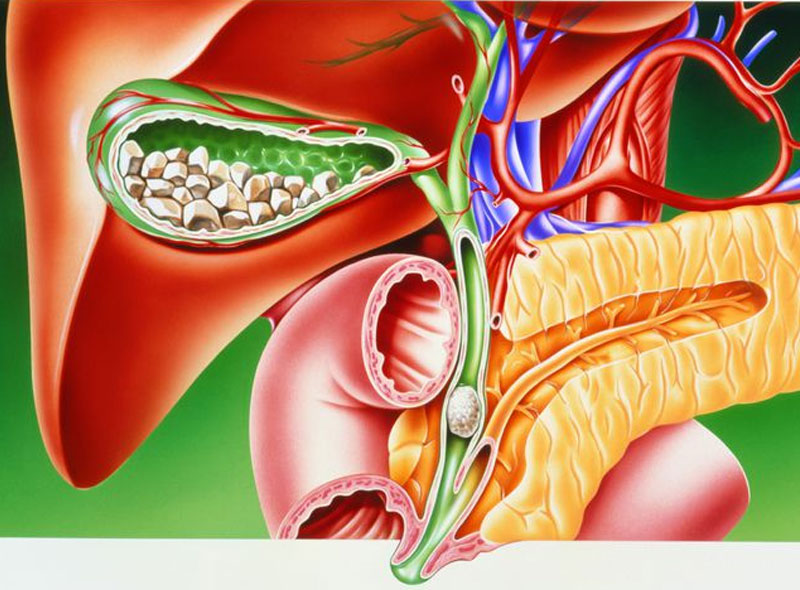
Common Bile Duct Stone
What is Common Bile Duct Stone (Choledocholithiasis, Cholangitis, Obstructive Jaundice) Choledocholithiasis is a disease of the common bile duct. The common bile duct forms at the junction of the cystic duct (from the gallbladder) and the common hepatic duct (from the liver). It drains bile into the duedenum (the first part of the small intestine).
Gallstones (cholesterol stones or pigment stones) form in the gallbladder over many years. They can sometimes travel into the common bile duct, causing a blockage. If the common bile duct is blocked, this then obstructs the whole of the biliary drainage system as opposed to a blockage further up. Hence there is nowhere for the bile to go but up and the patient becomes jaundiced since certain waste products (bilirubin) are absorbed back into the blood stream. Furthermore there can be potentially fatal complications of infection of the biliary tree (cholangitis) and acute pancreatitis.
Risk Factors for Common Bile Duct Stone (Choledocholithiasis, Cholangitis, Obstructive Jaundice)
The predisposing factors for common bile duct stones are the same as for Gallstones. Risk factors for cholesterol stones include: high serum cholesterol leves, increased age, female sex, obesity, rapid weight loss, the contraceptive pill, and total parenteral nutrition.Risk factors for pigment stones include chronic hameolysis (red blood cell breakdown) -hereditary spherocytosis, sickle cell disease, as well as liver cirrhosis. They may also form in the bile ducts after cholecystectomy (surgical removal of the gallbladder).