Fissure
What is an anal fissure?
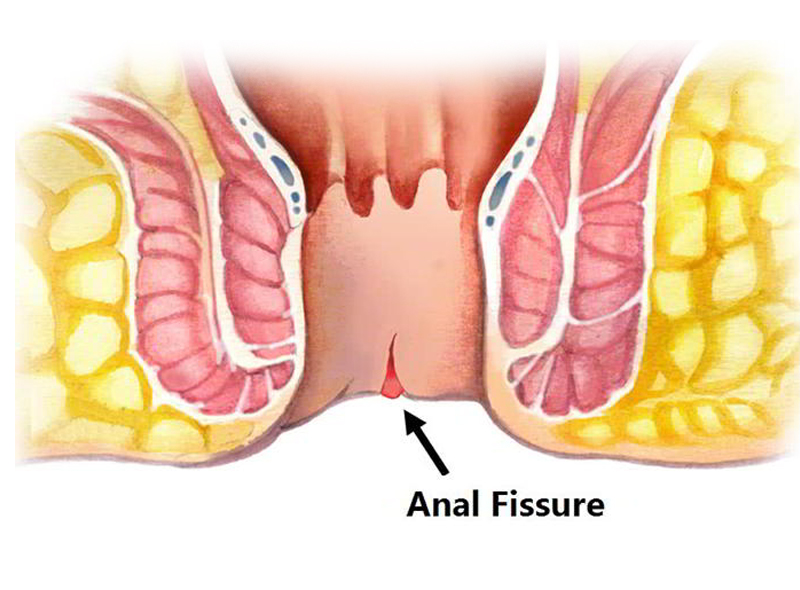
An anal fissure is a small cut or tear in the lining of the anus. The crack in the skin causes severe pain and some bright red bleeding during and after bowel movements. At times the fissure is deep enough to expose the muscle tissue underneath. An anal fissure may occur as a result of childbirth, straining during bowel movements, or long bouts of constipation or diarrhea. Anal fissures can also be the result of certain medical conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), infection, and cancer.
An anal fissure can affect people of all ages, and it’s often seen in infants and young children. Constipation is a common problem in these age groups. An anal fissure usually isn’t a serious condition. In most cases, the tear heals on its own within four to six weeks. In cases where the fissure persists beyond eight weeks, it’s considered chronic, or long term.
Certain treatments can promote healing and help relieve discomfort, including stool softenersand topical pain relievers. If an anal fissure doesn’t improve with these treatments, surgery may be required. Or your doctor may need to look for other underlying disorders that can cause anal fissures.
Symptoms
What are the symptoms of an anal fissure?
An anal fissure may cause one or more of the following symptoms:
- a visible tear in the skin around your anus a skin tag, or small lump of skin, next to the tear
- sharp pain in the anal area during bowel movements
- streaks of blood on stools or on tissue paper after wiping
- burning or itching in the anal area
Causes
What causes an anal fissure?
An anal fissure most often occurs when passing large or hard stools. Chronic constipation or frequent diarrhea can also tear the skin around your anus. Other common causes include:
- Crohn’s disease or another IBD
- straining during childbirth
- decreased blood flow to the anorectal area
- overly tight or spastic anal sphincter muscles